Comparing the transduction efficiency of two AAV vectors in RPE and Retinal Organoid models derived from iPSCs lines
Tissue
Retina ModelsThe Problem of the Client
We defined the problem and questions to be answered through in-depth discussion between the customer and our technical experts. The qualitative study needed to include the generation of a disease model that would allow comparison of transduction efficacy of 3 variants of 2 AAV vector serotypes in a disease setting.
Solution
Step 1:
Understanding the Problem
We defined the problem and questions to be answered through in-depth discussion between the customer and our technical experts.
The qualitative study needed to include the generation of an in vitro model retinal organoid (RO) model as well as one of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) both of which included a disease mutation to compare the transduction of 2 AAV vectors. It was necessary to define correct time points for testing as well as best imaging methods to allow for relevant comparison.
Step 2:
Developing a Customised Experimental Plan to Compare Transduction Efficacy
We designed a study in 2 parts and presented the plan to the client. The first part of the study consisted in generating and characterising retinal organoids and RPE from iPSCs containing the disease mutation of interest.
The second part of the study assessed the efficacy of the vectors through transduction of retinal organoids and RPE with the 2 AAV vector serotypes (3 variants for each) and also monitored transgene expression through live imaging and harvesting up to 28 days post transduction. When possible, the same image settings would be used to enable a direct comparison of the transgene expression levels.
Step 3:
Project Execution within 5 Months
Our scientists executed the agreed experiments providing regular updates to the customer.
Phase 1: Characterisation of retinal organoids and RPE
The retinal organoids were characterised by confirming the presence of all major cell types by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence. The characterisation of RPE was performed by morphological analysis with brightfield imaging and TEER measurement.
Phase 2: AAV transduction of retinal organoids and RPE
For each AAV vector, three variants were tested, each with 3 doses. Each data point was performed in triplicate. Transgene expression was monitored by fluorescence imaging from day 7 to 28 post-transduction. Organoids were harvested at 24h, 72 h, 7 days, 14 days, 21 and 28 days for analysis.
Output Dataset:
A

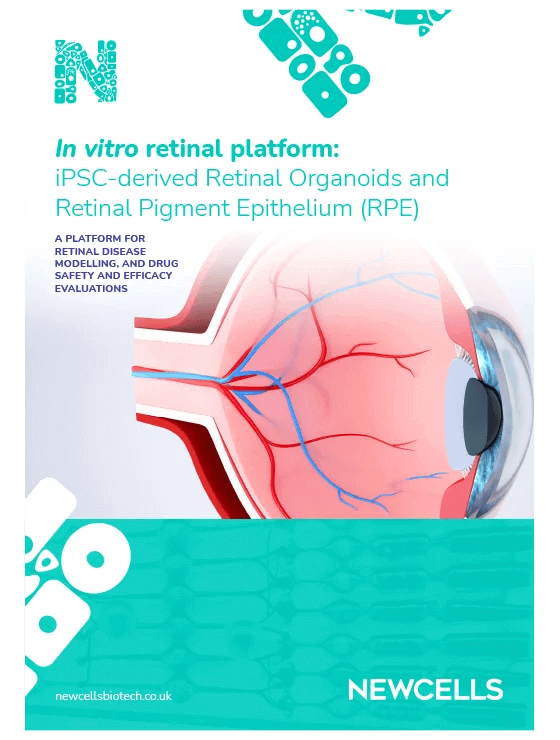
GFP immunofluorescence and brightfield images of RPE at days and 21 days post-transduction with AAV-A and AAV-B.
B
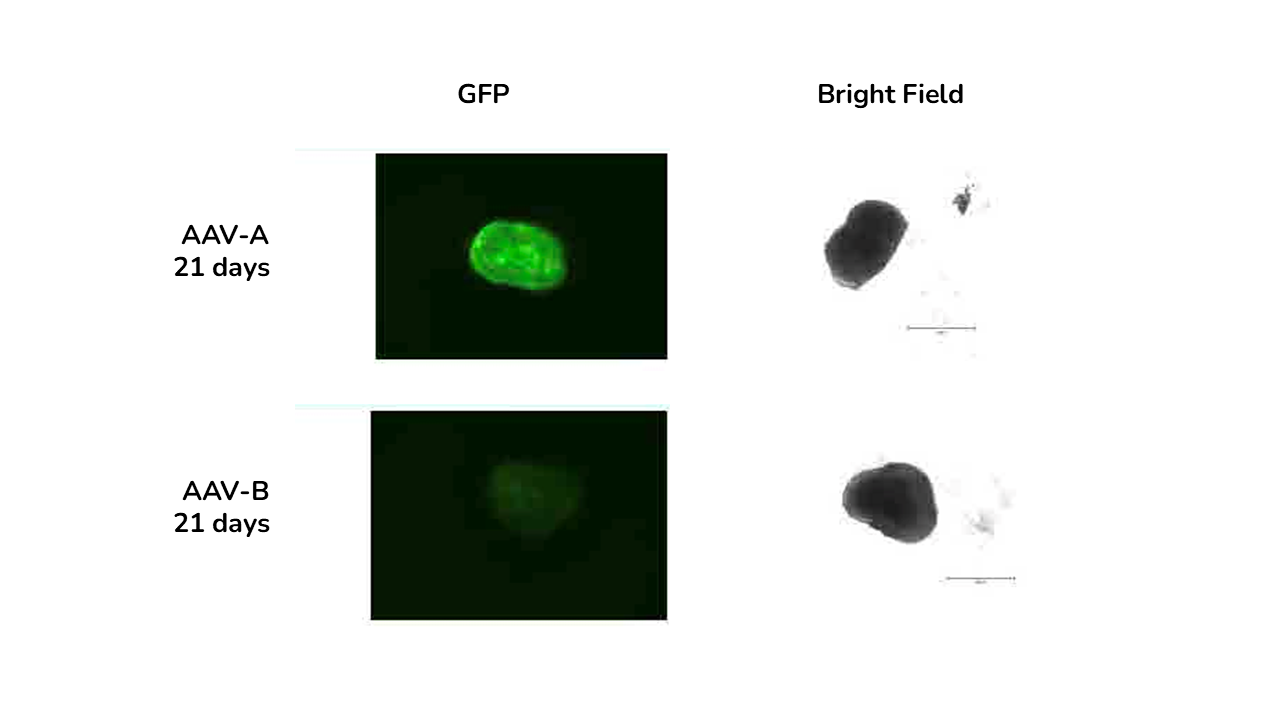
GFP immunofluorescence and brightfield images of retinal organoids at days and 21 days post-transduction with AAV-A and AAV-B.
The study showed that viral vector transduction was more efficient at the higher AAV dose, showing mostly transgene (GFP) expression in the neural retina layers of the retinal organoids. The study also showed cellular localisation of the vector with GFP staining colocalised with photoreceptor marker RCVRN at day 150 and not with bipolar cell marker VSX2.
Step 4:
Delivery of Results
We delivered a detailed report of the dataset which was shared digitally and discussed over a call.
The study clearly showed:
- The best variant was identified showing that AAV-A vector transfected retinal organoids and RPE more efficiently than AAV-B
- Higher transfection efficiency was obtained with higher AAV doses both in organoids and RPE
- Reporter gene expression increased over time from 7 to 28 days post transduction in both organoids and RPE.
- For retinal organoids, reporter gene expression was mostly -but not exclusively- localised in the outer organoid layers containing the neural retina.
Outcomes for the Client and the Project
The data allowed the client to confidently select the most efficient AAV vector for the transduction of diseased retinal organoids and RPE, allowing further development of the vectors of interest.