A functional monolayer in vitro model of retinal pigment epithelial cells generated from human iPSCs for accurate prediction of clinical outcomes
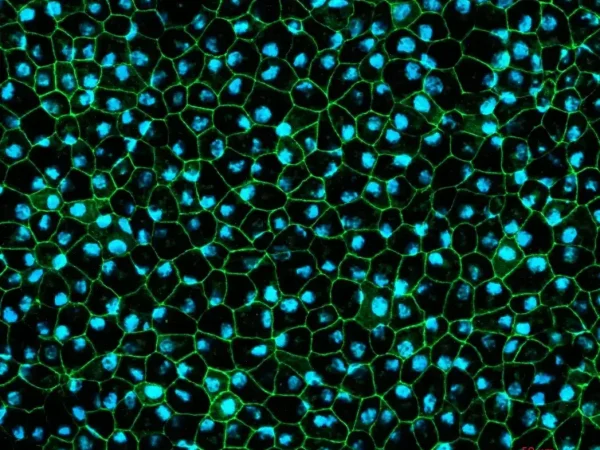
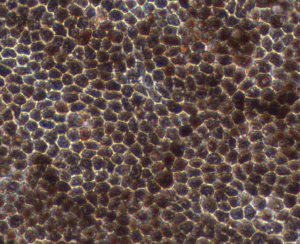
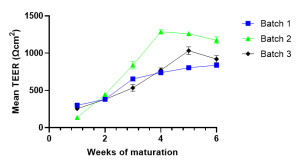
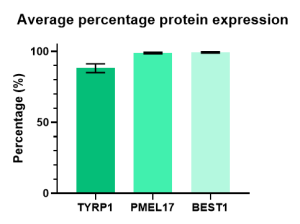
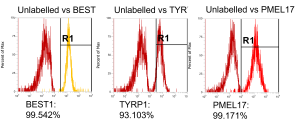
The retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell model, used for our services, is composed of a monolayer of RPE cells. Uniquely, our RPE cells are derived from healthy donor iPSCs from the same genetic background as retinal organoids, allowing parallel assessment of both RPE and neurosensory retina. We also have the capability to generate RPE cells from customer-supplied iPSCs. The 24-well Transwell® plates format allows for flexibility in dosing and analytical readouts, including functional assessment of the cells. The RPE characterisation is extensive including morphology assessment, pigmentation, RPE-specific expression at the protein level (BEST1, TYRP1), analysis of phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments, trans-epithelial resistance (TEER), polarity of apical Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factors (PEDF) and basal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion.
“The extensive scientific knowledge and rigor of Newcells’ staff in the field of ophthalmology as well as their client goal-oriented thinking allowed us to advance quickly in our proof of concept.” Dr Elke Vermassen, Sr. Product Development Manager, KiOmed Pharma
Applications
- Gene therapy including in vitro viral vector assessment
- Disease modelling
- Investigational drug safety and efficac
Available analytical readouts for services provided with RPE
- Imaging
- mRNA quantification by RT-qPCR
- Transcriptomics by single-cell RNA sequencing
- Growth factor (VEGF, PEDF) secretion
- Flow cytometry