Efficacy testing of novel therapies on predictive human in vitro retinal models
Retina efficacy study: this service evaluates how a compound or viral vector affects structure and function of retinal cellular models, by using Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) models. The outcome of these investigative retinal disease studies may support treatment methods for retina diseases like diabetic macular oedema or other problems like macular degeneration.
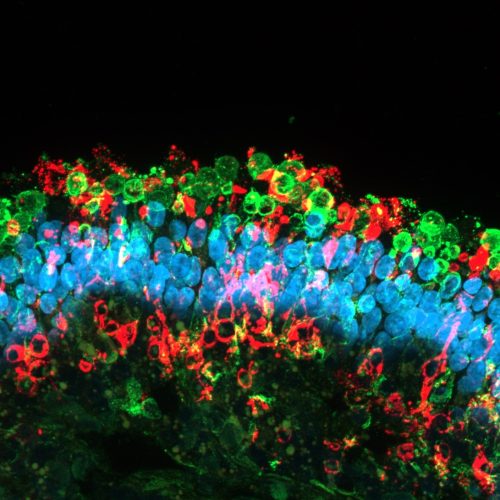
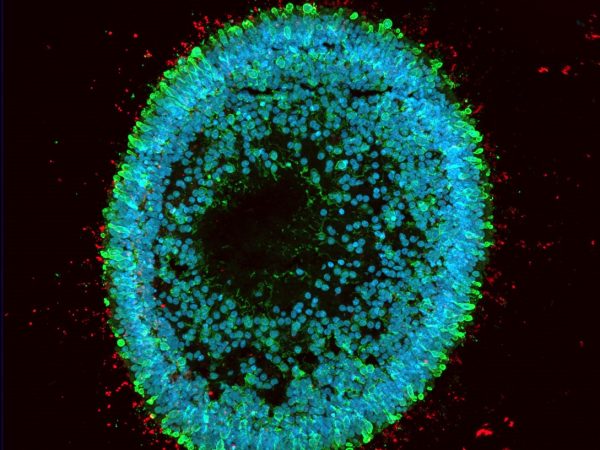
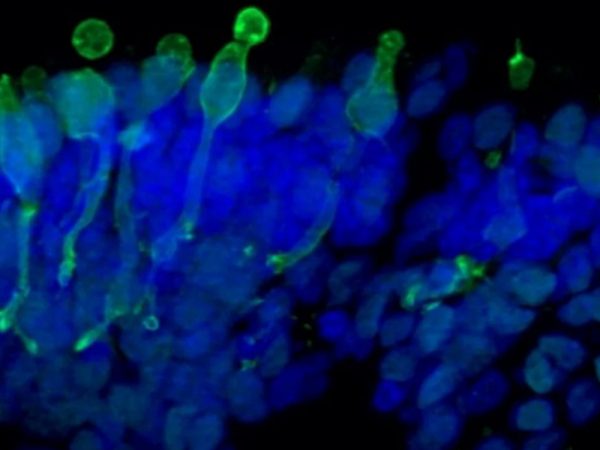
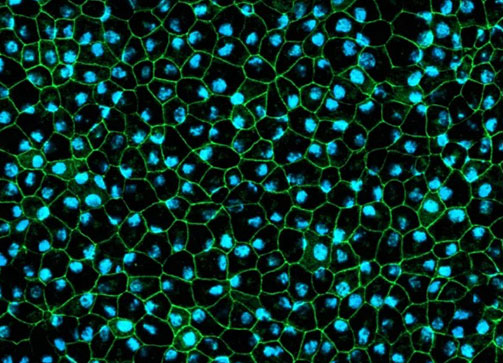
The in vitro drug efficacy study allows rapid evaluation of the efficacy of your drug on high quality healthy and/or diseased human IPSC-derived retinal organoids and/or RPE models. The models are highly representative of the structure and function of human retinal tissues and can also be generated from patients’ iPSCs or gene edited iPSC lines, thus facilitating predictive advanced in vitro testing of new therapeutics and accelerating lead compound selection.
The assays can be carried out at different time points of organoid differentiation and will provide predictive data to allow for confident decision making to progress your new drug or submit an IND.
Service outputs
- Rapid retinal efficacy evaluation of compounds in retinal organoids and RPE
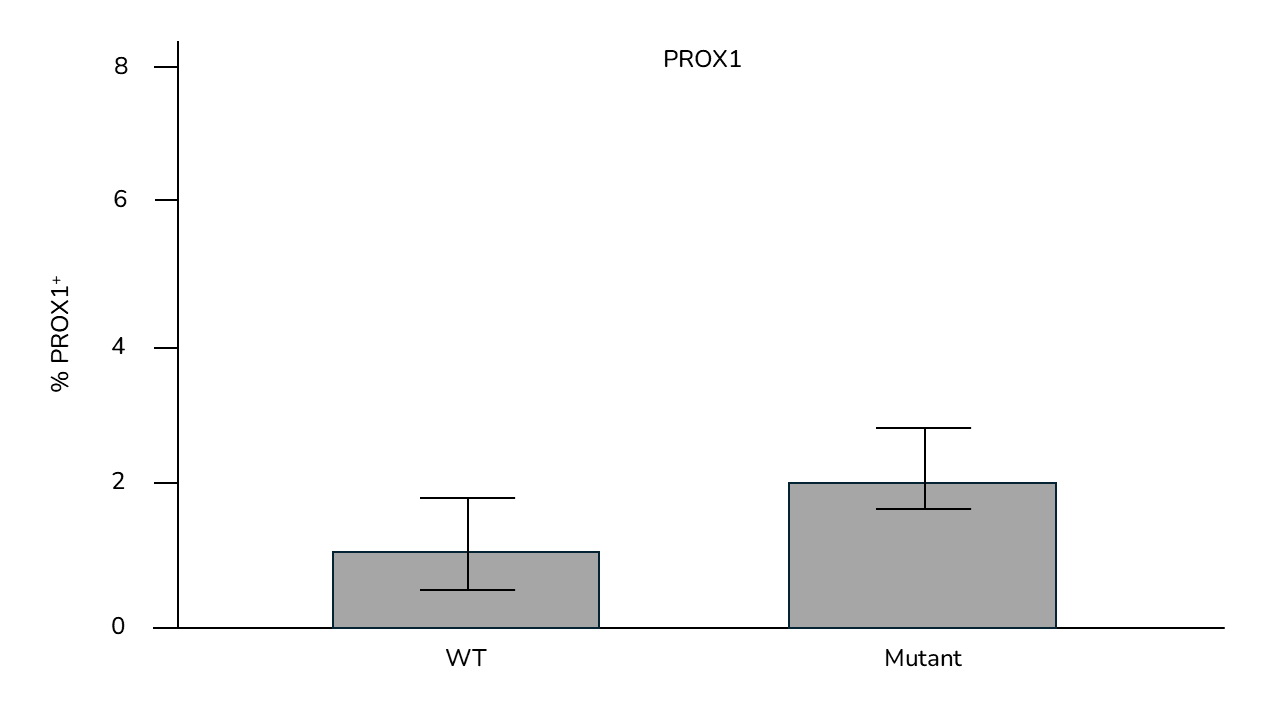
- Quantitative and qualitative analysis of key markers expression by gene expression analysis and immunofluorescence on frozen retinal organoid sections
- Time points comparisons
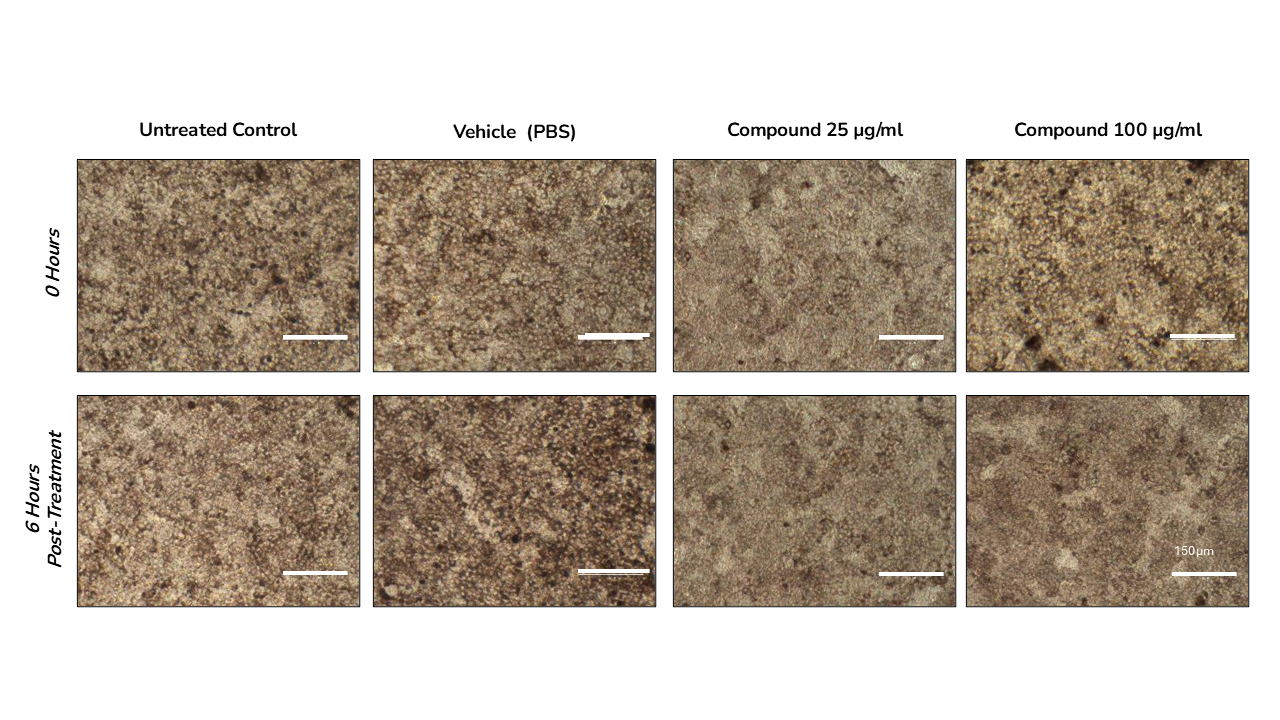
- Compound effect on PRE barrier, phagocytic integrity, viability and ultrastructure