Comprehensive toxicity study on retinal ganglion cells in early-stage human retinal organoids
Tissue
Retina ModelsThe Problem of the Client
The client wanted to analyse and quantify the effect of their compounds on survival of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) in early-stage organoids.
Solution
We ran a comprehensive toxicity study to test the effects of the compounds of interest on wild-type iPSC-derived human retinal organoids at an early stage of differentiation.
Step 1:
Understanding the Problem
Discussions between the client and our experts identified that it was essential for the study to assess toxicity in a specific region of the early retinal organoid microtissues enriched with ganglion cells and therefore use of retinal organoids at an early stage of differentiation.
Given the need for quantitative measurements, we agreed with the client that the study would include TUNEL staining and quantification of TUNEL images for localisation and intensity analysis with a customised Fiji software to perform statistical analysis of apoptotic cells.
Step 2:
Developing a Customised Experimental Plan
We designed a two parts study which was presented and agreed in our Statement of Work.
Part 1: Use of Hoechst staining for the identification of the apoptotic areas within the retinal organoids in the presence of the two test compounds.
Part 2: Quantification of the effect of two compounds and relevant controls through measurement of TUNEL florescence intensity on frozen 10 mm thin organoid sections.
Step 3:
Rapid Project Execution
Our scientists carried out the agreed experiments within the agreed timeline providing regular updates to the customer.
The study included the experimental phase, data processing, data analysis and presentation of a detailed data summary.
Output data set:
The study delivered qualitative and quantitative toxicity imaging data for:
- 2 compounds in buffer
- Positive control inducing apoptosis
- 2 Negative controls: Untreated and buffer only
6 technical replicates were performed per experimental condition.
The RGC layer and organoid core was distinguished from the outer organoid layer by fluorescent imaging based on Hoechst staining patterns. The images were acquired with the Zeiss Axio Apotome fluorescence microscope (20x objective).
The level of apoptosis was quantified through TUNEL assay using a Zeiss Axio Apotome fluorescence microscope (20X magnification).
Example data:
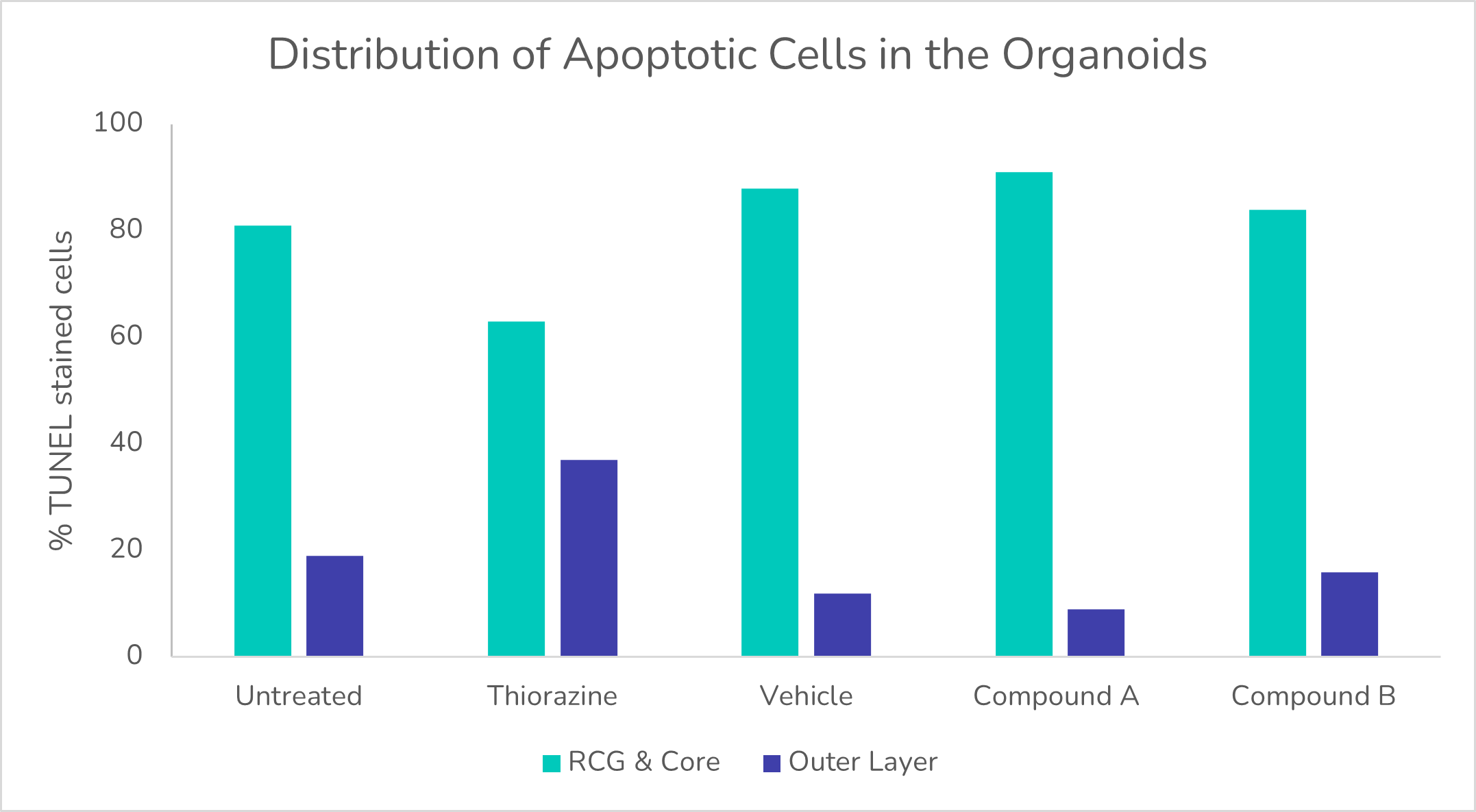
Distribution of apoptotic cells in the organoids.
Step 4:
Delivery of Results
We delivered a detailed report of the dataset which was shared digitally and discussed over a call.
The study report clearly demonstrated that:
- Known retina toxicant Thioridazine was used as a positive control and induced an expected increase in apoptosis in the outer region of the retinal organoids, where photoreceptors are present.
- Apoptosis was mostly localised to the retinal ganglions layer and the core regions, where necrotic cells are usually present for all conditions tested apart from the positive control.
- The compounds did not cause an increase in apoptosis or survival of retinal ganglion cells compared to treatment with buffer alone.
Outcomes for the Client and the Project
The study showed that the compounds did not accelerate apoptosis in retinal ganglion cells in early-stage organoids, allowing the client to make an informed decision with regards to the safety profile and progression of their compounds.