Predicting human renal injury from antisense oligonucleotide (ASO)
Tissue
Kidney Toxicity ServiceThe ask
Retrospective study: Evaluating if the nephrotoxicity of an antisense oligonucleotide detected during a human clinical trial could have been predicted in vitro.

Solution
We designed a customised set of experiments to answer the customer’s query.
Step 1:
UNDERSTANDING THE PROBLEM: EXPLAINING UNEXPECTED IN VIVO KIDNEY TOXICITY
We defined the problem and questions to be answered through in-depth discussion between the customer and our technical experts.
One of the ASO that had progressed to clinical trial triggered kidney damage, even though no nephrotoxicity was observed in preclinical animal models. The customer wished to find out if this effect could have been predicted using a human kidney proximal tubule cells model in vitro.
Step 2:
DEVELOPING A CUSTOMISED EXPERIMENTAL PLAN TO COMPARE 3 ASOS IN THE HUMAN MODEL
We designed the specific experiments and presented the plan in our Statement of Work.
The experimental plan defined how to compare three ASOs in the fully validated human proximal tubule cells model (aProximateTM).
The experimental plan consisted of
- adding the ASO to the kidney proximal tubule cells
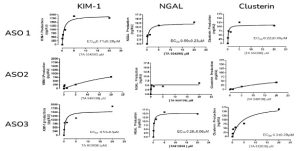
- assessing the effects on kidney injury biomarkers KIM-1m NGAL and Clusterin after 72h.
- evaluate the cell monolayer integrity through TEER measurement
- determine cell heath by measuring ATP, and cell death by LDH
Step 3:
PROJECT EXECUTION WITHIN 2 MONTHS
Our scientists carried out the agreed experiments within 2 months providing regular updates to the customer.
The study included the experimental phase, data processing, data analysis and presentation of a comprehensive data summary.
OUTPUT DATASET: 3 compounds, 1 positive control, 180 datapoints
Example data set that was provided to the customer
The study was completed in 2 months.
Step 4:
DELIVERY OF RESULTS
We delivered a detailed report of the dataset which was shared digitally and discussed over a call upon request.
The study clearly showed :
- ASO2 did not affect the production of kidney Injury markers KIM-1, NGAL or Clusterin, showing low kidney toxicity of the compound.
- ASO1 and ASO3 resulted in significant increase in all marker expression with EC50 values in the nanomolar range
- ASO1 and ASO3 also perturbed the monolayer integrity, cell health and triggered LDH release.
Outcomes for the client and the project
We delivered a robust dataset which clearly showed renal toxicity and kidney damage induced by ASO could have been predicted in vitro using human aProximateTM PTC, showing better accuracy than other preclinical animal models.