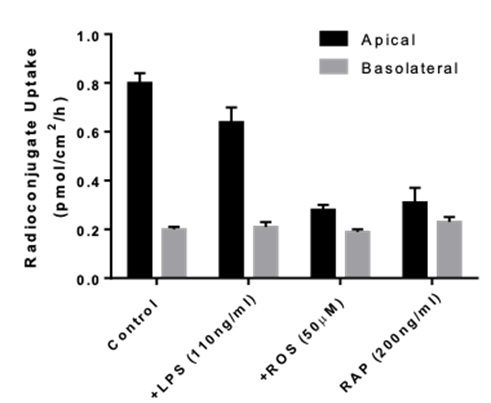Investigate renal drug transport modalities and drug interactions in vitro
Drug Transporter and Drug-Drug Interaction Study
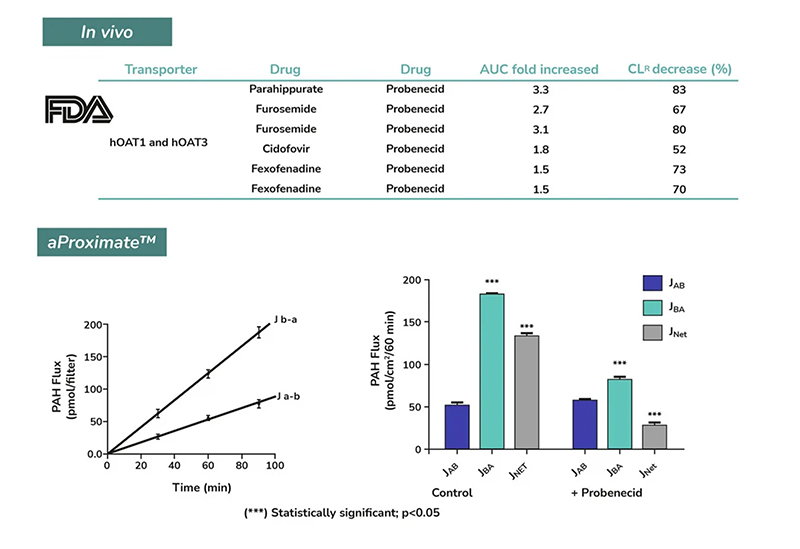
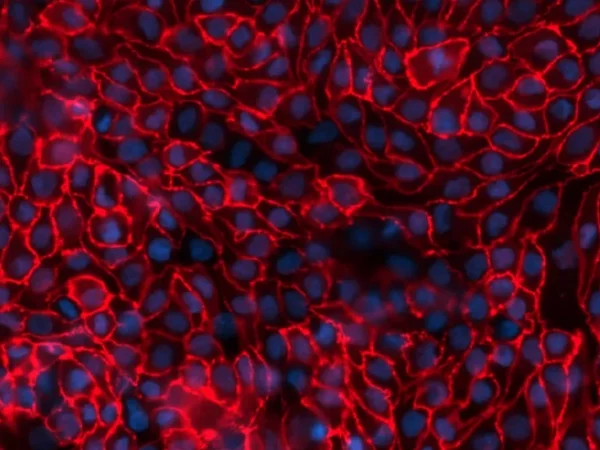
This service uses the aProximate™ Proximal Tubule Cell model, which retains high expression of the relevant transporters involved in drug handling, making it ideal for drug transporter and drug interaction studies. Using kidney transporter assays – sometimes referred to as renal transporter assays – this service supports drug-to-drug interactions by determining if one drug will affect the transport of another, potentially altering efficacy or kidney toxicity.
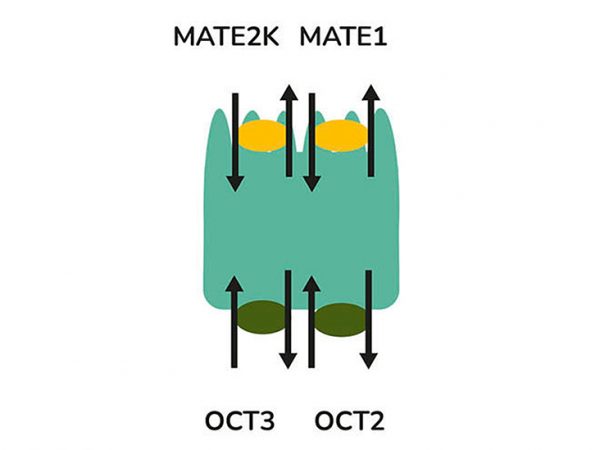
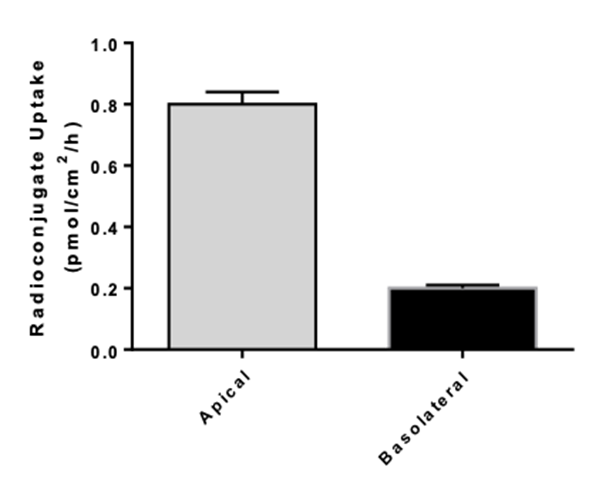
Transporters play a major role in the uptake and efflux of drugs across cellular membranes. Given the presence of Megalin and Cubilin in this kidney model, two key uptake transporters for large molecules, the model is particularly insightful to predict the transport or retention of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), antibiotics, anti-sense oligonucleotides (ASO) and radiolabelled conjugate in the proximal tubule.
Drug interactions with transporter proteins are common, and they can act either as substrates and/or inhibitors, a role which is best identified during the early stages of drug development to define the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) profile. Cross-species comparison between human, rat, mouse and dog can also be added as part of this service. Using our scientific expertise, Newcells provides advanced predictive kidney transporter assays to answer your specific requirements and understand potential drug-drug interactions of both small and large molecules.
Service outputs
- Flux Assay: Apical to Basal (Jab) and Basal to Apical (Jba) flux
- Net transport measurements
- Uptake assays : measurement of intracellular drug and metabolite concentrations
- Identification of transporter-mediated drug interactions
- High content imaging data